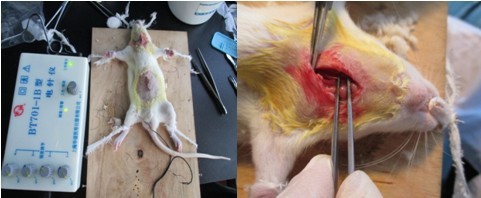
盲腸結扎穿孔以及電針刺激
1. SD大鼠適應性飼養一周
2. 水合氯醛麻醉,然后打開腹部,對盲腸用生銹的注射器針頭刺穿
3. 術后縫合,觀察動物狀態,并對電針組實驗動物進行電針治療
4. 在6h、12h分別處死部分動物取血
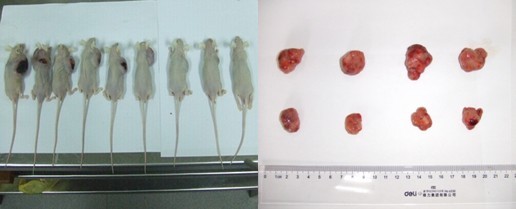
腫瘤模型(皮下種植結腸癌/肝癌/肺癌模型)
1. 購買4~6周的裸鼠,適應性飼養一周
2. 前肢腋下部位附近皮下種植結腸癌細胞,濃度1X107個/100ul
3. 注意無菌,然后飼養觀察
4. 稱重和實驗觀察和記錄
5. 一般實驗需要4周左右
大鼠心梗模型
1. 購買4-6周的大鼠,適應性飼養一周
2. 進行大鼠冠脈結扎,于末次給藥后1h,在戊巴比妥鈉腹腔麻醉下仰位固定于手術臺,自左側3-4肋間開胸,暴露心臟,于肺 動脈圓錐及左心房間找出冠脈左前降支,立即結扎冠脈,將心臟送回胸腔,并擠出胸腔內血液和氣體,迅速關閉胸腔,開胸時間不超過30s。術后5天連續注射青霉素鈉
3. 觀察開胸后、縫針后、結扎后、關胸后心電圖的變化
4. 合格后的大鼠在4周及6周后復查心電圖
自體靜脈移植
1. 選新西蘭大耳兔,戊巴比妥鈉按照體重麻醉
2. 切開頸部皮膚,鈍性分離皮下組織;選取大小和直徑同要移植部位的血管相同的靜脈血管,先結扎該靜脈的兩端
3. 剪下該靜脈,用滅菌生理鹽水沖洗干凈,備用
4. 將要移植部位的動脈血管,同周圍組織分離,兩端用動脈夾夾閉,然后剪下,把斷端清洗干凈;把前面的靜脈縫合到該動脈斷端。先稍微放開遠心端的動脈夾,檢查是否有滲血,確認無滲血后,同樣 方法檢查另外一端
5. 分層縫合,在關閉皮膚前,進行嚴格清潔和抗菌處理,然后縫合皮膚
6. 術后兩周內靜脈注射適量的肝素抗凝,隨時觀察實驗動物的狀態,及時處理;根據客戶自己確定實驗周期,準備動物和實驗器材至少需要一周
貼劑動物體外實驗
1. 實驗分組及處理
2. 用藥24h后取下,用溫水洗脫
3. 分別于1h,24h,48h,72h肉眼觀察局部有無紅斑和水腫。然后連續用藥7d,每天貼敷時間為12h,觀察停藥1h,24h,48h,72h后局部紅斑、水腫情況,以及是否有色素沉著、出血點、皮膚粗糙或皮膚菲薄等情況,記錄發生和消退時間
皮膚急性毒性試驗
1. 實驗分組及處理
2. 用藥24h后取下,用溫水洗脫
3. 分別于1h,24h,48h,72h至第7天,每天觀察并記錄動物的體重、皮毛光澤、飲食、眼和粘膜的變化,呼吸中樞、神經系統、四肢活動和死亡情況
4. 并于7天后處死大鼠,解剖觀察其心、肝、肺、腎、卵巢、子宮等臟器有無異常變化,詳細記錄任何組織或器官出現的體積、顏色、質地的改變
5. 主要臟器稱重,計算臟器指數
皮膚過敏試驗
1. 實驗分組及處理
2. 脫毛24h后,取痛經巴布貼貼敷在SD大鼠脫毛區,并以無刺激膠布固定,持續6h,第7天和第14天以同樣方法重復一次
3. 于末次給痛經巴布貼巴布劑致敏后14d,將痛經巴布貼貼敷于SD大鼠脫毛區,賦形劑貼對照組與陽性對照組方法同上
4. 6h后去掉受試藥物,即刻觀察,并于24h,48h,72h再觀察有無過敏反應,按表一記錄個時間過敏反應分值,同時注意觀察SD大鼠是否有哮喘、站立不穩或休克等嚴重的全身性過敏反應,計算致敏發生率
藥效學實驗
1. 實驗分組及處理
2. 采用戊酸雌二醇+催產素引起大鼠子宮收縮為痛經模型。大鼠灌胃0.8mg/只/天(第1天和第10天),其它時間0.4mg/只/天,連續15天,第15天腹腔注射催產素2u/kg
3. 一般行為觀察:精神狀態、活動度、體重、食量、死亡率等
4. 扭體反應發生率觀察:注射催產素后觀察30min扭體反應發生率
5. 療效觀察:各組模型大鼠子宮、卵巢精確稱重,計算子宮、卵巢指數
6. 觀察對模型大鼠血液流變學的影響
IBD模型
1. 造模前 1d 禁食 24h 不禁水稱重后,3%的戊巴比妥腹腔注射麻醉(或乙醚) 5%(W/V)的2,4,6-三硝基苯磺酸 (TNBS) 按 100mg/kg-150mg/kg(約等于TNBS 原液 0.4mL-0.6 mL,相當于 200 g 大鼠 20 mg-30 mg )
2. 分別加入乙醇,體位為頭朝下,用聚丙烯管插入肛門上段4cm 注射器注入
3. 再倒立1-5min左右,以防藥液溢出,每隔10d重復灌腸4次后可制成病鼠模型
4. 采血前觀察SD大白鼠的情況,記錄大鼠外觀體征、行為活動、糞便的情況,記錄死亡情況,每天稱重
MTD實驗
1. 動物稱重并標記
2. 計算相應給藥體積:按需計算每只動物的給藥量,分為高中低3個梯度,并作記錄
3. 給藥操作
4. 給藥后觀察:在給藥時記錄給藥時間。連續觀察至少14天,觀察一般指標(如動物外觀、行為、對刺激的反應、分泌物、排泄物等)、動物死亡情況(死亡時間、瀕死前反應等)、動物體重變化。記錄所有的死亡情況、出現的癥狀,以及癥狀起始的時間、嚴重程度、持續時間等
腎臟缺血再灌注
1. 購買200g的SD大鼠,飼養一周,分組
2. 根據體重注射相應劑量的水合氯醛,麻醉后進行手術
3. 打開腹腔,鈍性分離腎動脈,然后用動脈夾夾閉腎臟動脈30-45min,根據實驗者的設計執行
4. 然后去除動脈夾,腎臟再次流入動脈血,腎臟由紫黑重新變為鮮紅色
5. 然后根據實驗要求取材
成年營養性肥胖大鼠模型
1. 購買體重200g的雄性SD大鼠
2. 方法 :用高脂 高糖飼料喂養成年大鼠四至八周
3. 觀察大鼠體重及Lee’s指數、腹腔內脂肪重量及脂肪系數、葡萄糖耐量、血脂、血糖及血胰島素水平 ,并算出胰島素敏感性指數等
轉基因小鼠篩選——鼠尾提取基因組DNA方法
1. 小鼠分籠后打耳標,剪取小鼠尾尖3mm-5mm左右于1.5mL 離心管中,標記耳標號
2. 配置消化液(SSTE),每管加入消化液0.5mL,蛋白酶K 1-5 μL, 55℃,3-5h,或放置過夜。(最長可放置3天)
3. 加1倍體積(0.5mL)PCI(下層液體),上下顛倒10余次。(PCI可分裝出一些現用,以免操作不慎污染)
4. 室溫15000rpm離心,10min
5. 取上清約0.4mL入新管,依次標號,加入異丙醇0.4mL ,4℃,15000rpm離心,5min
6. 棄上清,濾紙吸干,加入70%乙醇0.5mL,將管底沉淀彈起,上下顛倒幾次,洗滌
7. 4℃,15000rpm離心,5-7min
8. 棄上清,瞬時離心,用槍吸干剩余液體,后經空氣干燥5-10min
9. 加入1*TE 60-170μL一般加100μL,振蕩30min溶解,于4℃冰箱保存
酶聯生物經過不斷的實驗優化和改進,積累了大量的經驗,擁有專業的酶聯研發團隊。利用專業的酶聯免疫技術自主研發的elisa試劑盒,能對血清及其它樣本定量檢測抗原,定性檢測特異性抗體。優質的試劑,先進的儀器和正確的操作是保證ELISA檢測結果準確可靠的必要條件。ELISA檢測的方便性、穩定性、重復性和可靠性方面都具有很大的優勢。
ELISA檢測技術服務內容:
1、雙抗體夾心法檢測抗原 2、間接法檢測抗體 3、為客戶提供各種ELISA技術進行樣本檢測。
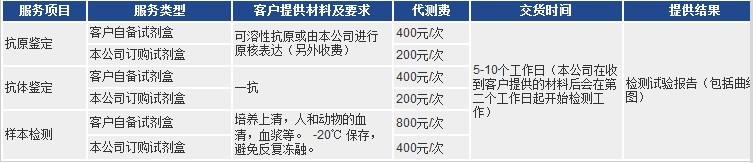
以上代測費,凡購買本公司試劑盒,我們免費代測!
凡購買本公司目錄任何一種酶聯免疫檢測試劑盒,您只需將需要檢測的動物(Human, Rat, Mouse, Rabbit, Monkey,
Pig……)種類和檢測指標(白介素類、激素類)及標本數量(48T/96T)通知公司業務員即可。在接到客戶標本當日起,現貨產品一周內將檢測報告交到客戶手中!
歡迎各科研單位在各種項目上與我們公司開展不同層次的密切合作,以雙贏求發展,共同進步,為中國檢測事業的發展積累經驗。
二、樣本要求
在收集標本前都必須有一個完整的計劃,必須清楚要檢測的成份是否足夠穩定。我們提倡新鮮標本盡早檢測,對收集后當天就進行檢測的標本,及時儲存在4℃備用,如有特殊原因需要周期收集標本,請造模取材后,將標本及時分裝后放在-20℃或-70℃條件下保存。因冰室與室溫存在一定溫差,蛋白極易降解,直接影響實驗質量,所以避免反復凍融。代測放免標本的客戶取材前須向我司銷售人員索要說明書,具體操作注意事項請與我司技術人員溝通。
液體類標本:標本必須為液體,不含沉淀。包括血清、血漿、尿液、胸腹水、腦脊液、細胞培養上清、組織勻漿等。
血清:室溫血液自然凝固10-20分鐘后,離心20分鐘左右(2000-3000轉/分)。收集上清。如有沉淀形成,應再次離心。
血漿:應根據試劑盒的要求選擇EDTA、檸檬酸鈉或肝素作為抗凝劑,加入10%(v/v)抗凝劑(0.1M檸檬酸鈉或1%heparin
或2.0%EDTA.Na2)混合10-20分鐘后,離心20分鐘左右(2000-3000轉/分)。仔細收集上清。如有沉淀形成,應再次離心。
尿液、胸腹水、腦脊液:用無菌管收集。離心20分鐘左右(2000-3000轉/分)。仔細收集上清。如有沉淀形成,應再次離心。
細胞培養上清:檢測分泌性的成份時,用無菌管收集。離心20分鐘左右(2000-3000轉/分)。仔細收集上清。檢測細胞內的成份時,用PBS(PH7.0-7.4)稀釋細胞懸液,細胞濃度達到100萬/ml左右。通過反復凍融,以使細胞破壞并放出細胞內成份。離心20分鐘左右(2000-3000轉/分)。仔細收集上清。保存過程中如有沉淀形成,應再次離心。
組織標本:切割標本后,稱取重量。加入一定量的PBS,緩沖液中可加入1μg/L蛋白酶抑制劑或50U/ml的Aprotinin(抑肽酶)。用手工或勻漿器將標本勻漿充分。離心20分鐘左右(2000-3000轉/分)。仔細收集上清置于-20度或-70度保存,如有必要,可以將樣品濃縮干燥。分裝后一份待檢測,其余冷凍備用。
三、寄標本時需注明以下情況:
1、標本編號;2、所測項目;3、是否做復孔;3、聯系方式;4、實驗后標本是否寄回。
客戶須知:
客戶應對所提供的材料及信息負責,如因客戶提供的材料及信息不準確而引起的實驗延誤或經濟損失由客戶承擔。
Q:1.
how to collect samples and preparation of ELISA?
Performed by ELISA test is generally common clinical samples including blood (finger
blood, blood), urine, feces, cerebrospinal fluid, pleural effusion, prostatic fluid,
semen, vaginal secretions, which
Some time of sample collection, preservation methods and has certain requirements.
Collection (a) clinical specimens
A, blood samples:Some physiological factors, such as smoking, eating, exercise, mood
swings, pregnancy, postural changes in blood can affect certain ingredients, even some
of diurnal variation. Therefore, blood samples
Acquisition should avoid interference physiological factors, consistent with appropriate
conditions, such as can not be avoided, should indicate the factors on the specimen.
1. Peripheral:Usually select the inside of blood left ring finger, the portion should be
no frostbite, inflammation, edema, damage. If the site does not meet the requirements to
other parts of the fingers instead. For burn patients, optional leather
Intact skin at the blood. As part of routine blood tests (eg, white blood cell count,
sort, etc.) affected by physiological factors fluctuation is too large, when compared to
the conditional should be consistent. It relates to the body, blood clotting function
Can test items (such as platelet count, bleeding time or clotting time) testing, we must
pay attention to understand whether the patient used anticoagulant, procoagulant drugs
in order to reduce or avoid interfering factors
influences.
2. Blood:In addition to involving a variety of projects such as hemostasis and
thrombosis detector requires the use of anticoagulated blood plasma, the current
analysis to detect the vast majority of projects can be directly detected using blood
serum. In the serum test items
, Some (such as blood sugar, blood fat) diet and circadian factors influenced, fasting
blood samples were generally appropriate; some decay rapidly in the blood (serum enzyme
activity assay such as ACP activity, etc.),
0 ~ 4 ℃ storage is not an activity decreased, the detection of these projects must be
timely and fast; some (such as creatine kinase) influenced by exercise and other
factors. Avoid hemolysis occurs when blood is also important
And, more particularly potassium, LDH and other measurement.
B, urine samples:With the same blood samples, urine samples affect diet, exercise,
medication and other factors that are also large, especially on the diet, so the morning
urine generally superior to random urine. Means getting up early morning urine
After the first urine specimens, representing concentrated and acidified visible
components (such as blood cells, epithelial cells, tubular) easy to observe the relative
concentration. Random urine that is a random urine specimens convenient, but by diet,
Sports, and even more the influence of drugs, prone to false positive and false negative
results, such as diet proteinuria, glucosuria diet, vitamin C interference occult blood
results and the like. Postprandial urine (patient 2 hours after lunch, collected
Human Urine) suitable for urine, urine protein and urobilinogen check urine samples at
this time to increase the sensitivity of the test, the detection of minor lesions. 12
hours in urine cell count is Addis count (last night 8:00
After emptying the bladder to all specimens of urine 8 o'clock the next morning),
because a long time, easy to breed bacteria shall be added preservative formaldehyde.
24-hour urine (the first day of the morning after emptying the bladder specimens from
8:00 to 8:00 the next morning
All urine) quantification of chemical substances, including proteins, sugars, urinary
17-one, 17-hydroxy steroids, catecholamines, Ca2 +, etc., to detect different
substances, choose a different preservative preservative. clean
Urine used for urine bacterial culture requires sterile specimens were taken after
washing the vulva. Urine specimens should be enough to collect all, at least 12 ml,
preferably 50 ml, the timing must collect all the urine of women
Patients should avoid vaginal secretions, blood contamination of urine specimens.
C, stool samples:Stool samples for the detection judgment digestive diseases has
important reference value. Collection requirements with a clean bamboo select faecal
mucus, pus and blood components and other abnormality, no abnormal appearance
Droppings shall be drawn from multiple surface and deep manure end. Get parasitemia and
for egg counts should be collected 24 hours feces. Dysentery amoeba trophozoites check
should immediately check in after a bowel movement, and from there sepsis
Softer at the drawn, insulation inspection. Charles S. japonicum eggs should take mucus,
pus and blood portion 30g stool specimens from at least miracidia hatching, and to be
treated as soon as possible. Check pinworm eggs must use transparent film swab
Night before 12:00 or early in the morning from defecation wrinkled folds around the
anus and immediately swabbing at microscopic examination. Occult blood test (chemistry),
fasting before the test on the 3rd of meat and foods containing animal blood and ban
clothing iron, vitamin C and so on.
Should be checked in all 1 hour stool specimen collection is completed, in order to
prevent damage to physical components of digestive enzymes and pH by. For clinical
samples above the detection indicators.
D, CSF samples:CSF samples collected immediately after submission, place too long will
affect the test results: such as cell degeneration, destruction, leading to counting and
classification are not allowed; some chemicals such as glucose content will decompose
Save
Less; bacteria occur autolysis affect bacteria detection rate. Cerebrospinal fluid
extracted three general dispensing a sterile tube, the first tube for bacterial culture,
a second tube for chemical analysis and immunological tests, the third tube for general
Characters and microscopic examination, three of the order should be reversed. Specimen
collection is difficult because all inspection and testing process should pay attention
to safety.
E, ascites and pleural effusion samples:CSF samples with the same attention to safety
after the specimen collection, and timely submission. Generally separated into three
tubes, one for routine cytology, a biochemical examination, a bacterial culture, in
order
CSF same is appropriate.
F, prostatic fluid sample:Prostatic fluid specimen after prostate massage by the
acquisition, directly drop when less liquid on a glass slide and timely submission shall
be taken to prevent sample evaporation to dryness, the amount collected for a long time
in a clean, dry test tube. If massage
No prostatic fluid, urine sediment can be checked after the massage.
G, semen samples:Abstinence before semen collection should be 3 to 7 days, drain the
urine after masturbation or other available methods of semen directly into clean
containers, insulation and timely submission. Due to changes in sperm production during
the day and
Large, generally should be checked 2 to 3 times (each time interval of 1 to 2 weeks) in
order to make a diagnosis.
H, samples of vaginal secretions:Vaginal samples were collected 24 hours before
intercourse should be prohibited, bath, vaginal examination, vaginal lavage and local on
the drug, etc., drawing instruments used need to be cleaned. Usually with brine-soaked
cotton swab from the vagina deep
Or rear vaginal fornix, cervical canal mouth drawn, etc., made after saline smear
vaginal secretion samples observation, women with menstrual vaginal secretions were not
checking.
2, do before each sample by ELISA experiment how to prepare?
Before collecting the sample must have a comprehensive plan must clearly be detected
component is stable enough. To be collected on the same day
Sample testing, and timely backup stored at 4 ℃. For the next day re-testing samples
frozen in a timely manner after dispensing -20 ℃ spare, conditional, preferably -70 ℃
cryopreservation standby. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing specimens
.
Liquid samples: including serum, plasma, urine, pleural effusion, cerebrospinal fluid,
cell culture supernatant and the like.
1. serum:
Coagulation at room temperature 10-20 mins, centrifugation 20 minutes or so (2000-3000
rev / min). Carefully collect the supernatant. If precipitation during storage,
Centrifugal again.
2. Plasma:
EDTA should be selected according to the requirements of the specimen, sodium citrate or
heparin as an anticoagulant, mix 10-20 mins, centrifugation 20 minutes or so (2000-3000
rev / min). Carefully collect the supernatant. Save process
If precipitation appeared, Centrifugal again.
3. Urine:
Sterile collection tube. Centrifuged for 20 minutes or so (2000-3000 rev / min).
Carefully collect the supernatant. If precipitation during storage, Centrifugal again.
Pleural and peritoneal effusions, and cerebrospinal fluid Reference to this practice.
4. The cell culture supernatant:
The detection of secretory component with a sterile collection tube. Centrifuged for 20
minutes or so (2000-3000 rev / min). Carefully collect the supernatant.
5. cultured cells
????When the detection of intracellular components, diluted with PBS (PH7.2-7.4) cell
suspension, the cell concentration reached 1 million / ml or so. By repeated freezing
and thawing or tissue protein extraction reagent was added to the cells
Damage and release of intracellular components. Centrifuged for 20 minutes or so
(2000-3000 rev / min). Carefully collect the supernatant. If precipitation during
storage, Centrifugal again.
6. tissues
????After cutting samples, check the weight. Adding a certain amount of PBS, PH7.4.
Rapidly frozen with liquid nitrogen. After thawing samples remained at 2-8 ℃. Adding a
certain amount of PBS
(PH7.4), or tissue protein extraction reagent, or by hand homogenizer homogenized
sample. Centrifuged for 20 minutes or so (2000-3000 rev / min). Carefully collect the
supernatant. A new package to be detected, which
I alternate freezing.
Q:Do
I have to run all of my standards and samples in duplicate?
A:Yes, the duplicates are run in order to monitor assay precision and increase
confidence in the assay results obtained.
Q:Do
I have to run all of my samples at one time?
A:No, each kit uses stripwell microplate. This allows the user to analyse different
numbers of samples at different times.
Q:What
types of reproducible results are obtained with the assays?
A:Each kit comes with a manual containing a graph of typical data obtained. Any
variation in operator, pipetting and washing technique, incubation time or temperature,
and kit age can cause variation in result. Each user should obtain their own standard
curve.
Q:Is
it possible to store the reagents other than indicated?
A:Storage of the kit components under conditions other than indicated is not recommended
in order to assure proper performance of the test.
Q:How
should I store my samples?
A:Samples should be stored at -20oC or lower temperature. For long-term storage, it is
recommended to freeze them at -70oC -80oC.
Q:Can
I modify the protocol?
A:BG ELISA kits have been optimized to provide the best possible results. Modifying the
format or protocol may give inaccurate and wrong results.
Q:Can
I use a sample type that is not recommended in the kit insert?
A:The kit has been validated for the sample types listed in the kit insert. Sample types
other than those validated have not been tested. Contact Technical Service for further
information.
Q:My
samples generated values that were outside the dynamic range of the assay. Can I use
these values?
A:It is recommended that only sample values that fall within the range of the standard
curve be used. Values outside the range of the standard curve are generally non-linear,
which can lead to incorrectly extrapolated values. Samples that generate values higher
than the highest standard should be (further) diluted and the assay repeated. If samples
fall below the range of the assay, the sample is considered to be non-detectable.
Q:Do
I have to run a Blank or Zero Standards every time?
A:Yes, these are required for the calculations, and reflect any subtle but significant
performance changes from day to day and assay to assay. They are also extremely helpful
when troubleshooting the source of a particular assay problem.
Q:Can
I alter the volume of sample I use in the assay?
A:It is not recommended that you alter the volumes since all BG kits are designed for
optimal performance at the given volumes
Q:Can
components from different kits be used?
A:Each kit contains components which have specific lot numbers to ensure that all of the
components are performing optimally alone, as well as with all of the other components
in the kit. QC testing is performed on these specific lots. It is never recommended to
use your own components or components from other kits or vendors.
Q:My
standard curve looked fine, but I didn’t get a signal in my sample when I expected
to, why?
A:The sample may not contain the analyte. A matrix effect may be masking the detection.
Ensure that the recommended dilution was followed as stated in the kit insert. If
dilution was recommended, check to be sure that the dilution was performed properly.
Over-dilution may cause the sample to fall below the range of the standard curve.
Q:How
do you recommend I wash my plate?
A:If you are using an automated plate washer we recommend that the calibration be
checked on a regular basis, and that the system is flushed with the Plate Washing Buffer
prior to washing. The same is true for a manual washer. A repeater or a wash bottle can
also be used. The user should be careful to ensure that all of the contents are
aspirated and the plate tapped dry on lint-free paper.
Q:Do
I need to use a plate shaker?
A:Reliable results can be obtained without a plate shaker, but the O.D.'s will generally
be lower than those obtained using a plate shaker.
Q:Why
do I have to use wavelength correction between 450-570nm?
A:For the ELISA assay, reading at dual wavelengths is done to correct for the optical
density contributed by the plastic well, the lamp and optical fluctuations.
Q:If
I extract my sample, do I still need to follow the recommended dilutions given in
the kit insert?
A:The amount of sample dilution needed after an extraction procedure will be affected by
the effects of purification and concentration in the protocol used. The amount of
dilution or concentration will have to be determined by the end-user.
Q:What
is the expected concentration of analyte that I should expect to find?
A:The amount of a given analyte may vary not only from species-to-species, but also
between tissue and cellular sources. The best source of this information is the current
literature that is easily accessed through the Internet at multiple scientific
databases.
Q:My
optical densities were a little higher (or lower) than those in the manual that came
with my kit. Why?
A:The optical density is affected by a number of physical conditions such as time and
temperature. We suggest that you shorten or lengthen the final incubation with substrate
solution to compensate.
Q:What
are the reasons for High Background?
A:1) Improper Washing: Check volume of washing buffer reservoir and make sure all
recommended washing steps are performed.
2) Contaminated Substrate: Make sure there is no contamination of the substrate with
metal ions or oxidizing reagents, before use. Keep the extra substrate solution
separately during the ELISA substrate development time.
3) Substrate exposed to light: Exposure to light may result in a blue color of the
substrate. Keep solutions in the dark (vial) until ready to dispense into the plate.
4) Wrong Incubation Times/Temperatures: Generally follow the test protocol regarding
incubation times and temperatures. However, if all wells are intensely and equally
colored with no intensity gradient observed in the standard dilution series, then it may
be necessary to observe the substrate reaction as the color is developing, in order to
stop the reaction sooner.


 酶聯官方手機二維碼
酶聯官方手機二維碼